WHAT'S INSIDE A BULLETPROOF VEST
By : TJ-OUTDOORS 2024-06-18Throughout history, humans have sought to shield themselves from injuries using various materials and technologies. Initially, animal skins were used for protection. With the advancement of weaponry, defensive measures evolved to include wooden and metal shields in their arsenals.
THE MAKE OF BULLETPROOF VESTS: MATERIALS USED
Have you ever wondered how law enforcement or security professionals protect themselves from bullets? They rely on discreet protection in the form of bulletproof vests! These innovative suits of armor shield them during risky operations or while carrying out official duties. But what specific materials are used to construct a bulletproof vest?
This blog post will investigate the materials utilized in bulletproof vests and the process used to manufacture this life-saving equipment. We will also discuss the properties of these materials and the technologies applied to increase their effectiveness.
THE HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF BODY ARMOR
During the 1800s, the Japanese pioneered softer body armor crafted from silk. While effective, the high cost led to the development of the flak jacket during World War II. Constructed from ballistic nylon, flak jackets offered protection against ammunition fragments. Despite their bulkiness and limited defense against rifle and pistol fire, they gained popularity for providing a sense of security to soldiers.
EXPLORATION AND ADVANCEMENTS
Through continuous research and development efforts, a pivotal moment arrived in 1960 with the emergence of a new fiber that enabled the creation of the Bullet Resistant Vest. This fiber boasted exceptional strength and introduced additional waterproofing capabilities, alongside layered fabrics that significantly improved the vest's durability and comfort. In subsequent years, The National Institute of Justice rigorously tested multiple versions of these vests and confirmed their ability to halt common bullets such as 38 Specials and 22 Long Rifle Bullets.
ADVANCED MODERN BODY ARMOR
Body armor is typically composed of Kevlar, Steel, Polyethylene (PE), or Ceramic materials. Soft body armor is primarily made from Kevlar and PE, whereas hard body armor utilizes steel and ceramic. Kevlar stands out for its lightweight properties and superior strength compared to steel.
Modern ballistic vests feature multiple layers of strong fibers designed to capture and distort bullets, often causing them to mushroom upon impact. This deformation spreads the bullet’s kinetic energy across a wide area of the vest's fibers. Although some layers may be breached, the bullet’s deformation ensures that energy is absorbed by an increasingly larger fiber area. While these vests prevent bullet penetration, they still absorb the bullet’s momentum, potentially causing blunt force trauma measured as back face signature.
MODERN BODY ARMOR DESIGNS




ADVANCED MODERN BODY ARMOR DESIGNS
Bulletproof vests are constructed with multiple layers to enhance their resistance to ballistic threats. The primary objective is to diminish the kinetic energy of bullets and disperse it, thereby preventing penetration. Let's delve into the layers commonly found in bulletproof jackets:
1. Outer Shell: The outermost layer shields the inner components from elements such as water, heat, and UV rays. It is typically crafted from abrasion-resistant fabrics like nylon or polyester.
2. Impact Absorption Layer: Positioned just beneath the outer shell, this layer disperses impact force over a wider area, effectively reducing the risk of blunt injuries. Common materials used include foam or other energy-absorbing substances.
3. Ballistic Materials: The primary bullet-resistant capability comes from ballistic materials, such as:
o UHMWPE Fiber: Known for its extraordinary strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding tensile strength. It absorbs and disperses a bullet's impact efficiently.
o Kevlar: Celebrated for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior tensile strength. It offers a protective layer that is light and strong, efficiently diffusing the impact of a bullet.
o Silicon Carbide: Recognized for its unmatched hardness and impenetrable resilience. It withstands and neutralizes the force of an impact effectively.


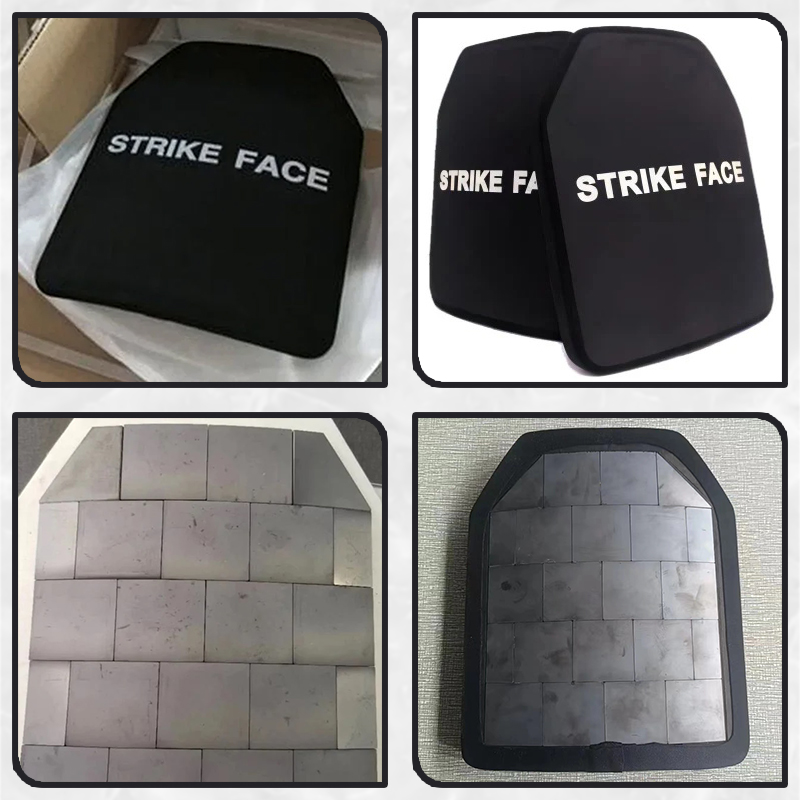
4. Backing Material: Positioned as the deepest layer, it provides durability, supports structural integrity, and prevents ballistic material deformation upon impact. Common materials include aramid fibers, UHMWPE, or a combination of both.
THE IMPORTANCE OF BULLETPROOF VESTS
Life is invaluable, and protecting it is paramount. Purchasing essential bulletproof vests from various sources can involve risks. However, with a TJ-OUTDOORS bulletproof vest, such concerns are unnecessary. TJ-OUTDOORS, a reputable defense company with over a decade of expertise in designing and manufacturing body armor, delivers high-quality products to effectively safeguard lives. You can place your complete trust in us. Our ordering procedures are straightforward and user-friendly.
FURTHER IMPROVEMENTS IN BULLETPROOF VESTS
Manufacturers are always finding new ways to make bulletproof vests better. Here are some of the latest improvements:
1. Hard Plates: For extra safety, vests can have hard plates. These are usually made from ceramic or hard steel and fit into pockets in the vest, helping to stop high-velocity bullets.
2. Soft Armor Panels: Often made from aramid fibers or UHMWPE, they protect important areas like the sides, shoulders, and collar while allowing easy movement.
3. Multi-Hit Capability: Modern vests are built to handle multiple hits without losing protection. Their layered design and special materials ensure they stay effective after several impacts.
4. Stab and Spike Protection: Some vests also protect against sharp objects like knives. They have extra layers made from materials like laminated Kevlar or metal alloys for added security.
HOW BULLETPROOF VESTS ARE MADE
Understanding what bulletproof vests are made of helps us appreciate their complexity. Here’s a look at how these vests are made:
1. Design and Pattern Development: The process starts with designing and creating patterns for the vests. Designers and engineers determine where and how many protective panels to place, based on specific ballistic threats.
2. Material Selection and Cutting: After the pattern is ready, layers of UHMWPE, Kevlar, or Silicon Carbide are cut into specific shapes and sizes using computer-controlled machines.
3. Layering and Assembling: The cut layers are then put together to form protective panels. Each panel has multiple layers of material, oriented in different directions to better absorb impact energy.
4. Sewing: The panels are sewn together with high-strength threads using heavy-duty sewing machines. Proper sewing techniques and thread tension are critical to ensure the vest's durability and effectiveness.
5. Final Assembly: Additional parts like straps, fasteners, and closures are added to the vest to ensure a secure and comfortable fit.
6. Testing and Quality Assurance: Each vest undergoes rigorous testing to meet safety standards and resist ballistic impacts. Quality control ensures the vest’s reliability and effectiveness in real-world conditions.
Bulletproof vests are essential for protecting those who serve and safeguard our communities. They demonstrate the innovation and dedication involved in creating life-saving gear for high-risk jobs. Using advanced materials and precise manufacturing techniques, these vests offer maximum protection.
relative Products
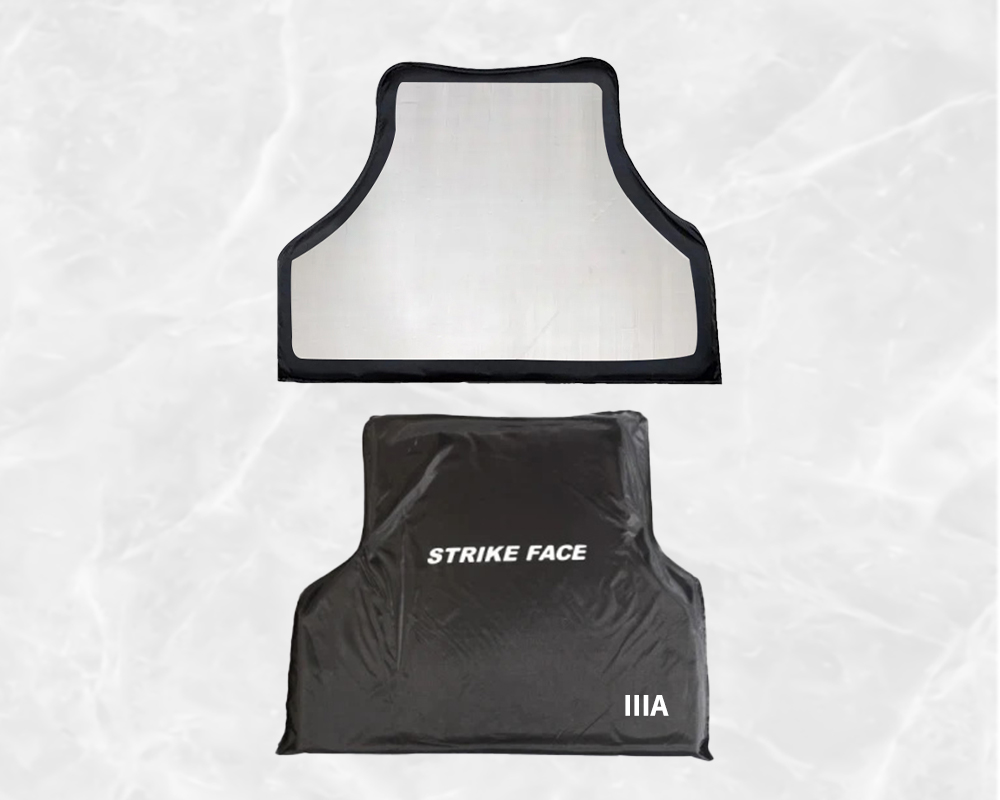 NIJ IIIA UHMW-PE bulletproof soft armour plate
NIJ IIIA UHMW-PE bulletproof soft armour plate
 NIJ III/IV SIC & UHMW-PE Ceramic bulletproof armour plate
NIJ III/IV SIC & UHMW-PE Ceramic bulletproof armour plate
 Plate Carrier Adjustable Quick release system Coyote Tactical Vest
Plate Carrier Adjustable Quick release system Coyote Tactical Vest
 NIJ IIIA Full protective body armor 1000D nylon/polyester military ves
NIJ IIIA Full protective body armor 1000D nylon/polyester military ves
 Aramid Fiber Kevlar material Bulletproof Fiber High-Strength Factory Direct Supply
Aramid Fiber Kevlar material Bulletproof Fiber High-Strength Factory Direct Supply
 PE Ud UHMWPE Weftless Cloth/UHMWPE Ud Composite for BulletProof and ExplosionProof
PE Ud UHMWPE Weftless Cloth/UHMWPE Ud Composite for BulletProof and ExplosionProof