In the intense environments of conflict and law enforcement, personal protective equipment (PPE) transcends the role of a mere defense; it acts as an unwavering bulwark, vigilantly guarding the boundary between danger and safety. At the forefront of this protective arsenal are two pioneering materials: Aramid (commercially known as Kevlar) and Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMW-PE). This comprehensive study presents a sophisticated comparative analysis, exploring the strengths and vulnerabilities of these materials, their historical evolution, technological advancements, and ecological impacts.
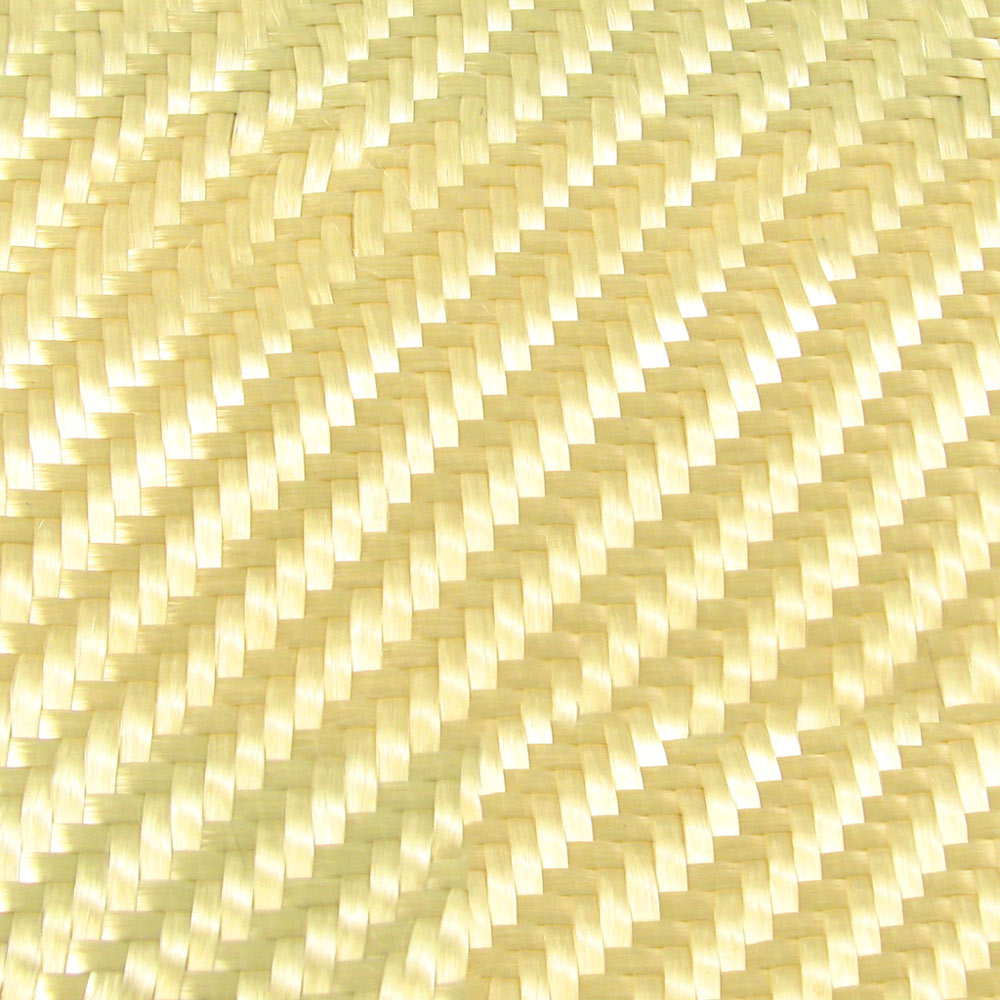
Aramid: The Time-Tested Guardian
- Introduction and Branding: Launched in the late 1960s as Kevlar, Aramid has been the preferred choice for bulletproof gear.
- Properties: It boasts a combination of heat and corrosion resistance, exceptional tensile strength, and a lightweight composition.
- Protection: Aramid's ability to absorb and dissipate impact energy has made it a key protector on numerous battlefields and in law enforcement.

Challenges with Aramid: The Achilles' Heel
- UV Sensitivity: Its vulnerability to UV light can degrade its structural integrity, reducing its protective capabilities over time.
- Hydrolysis Susceptibility: Aramid's reaction with water can weaken the fibers and shorten its service life, especially in high UV or humid conditions.
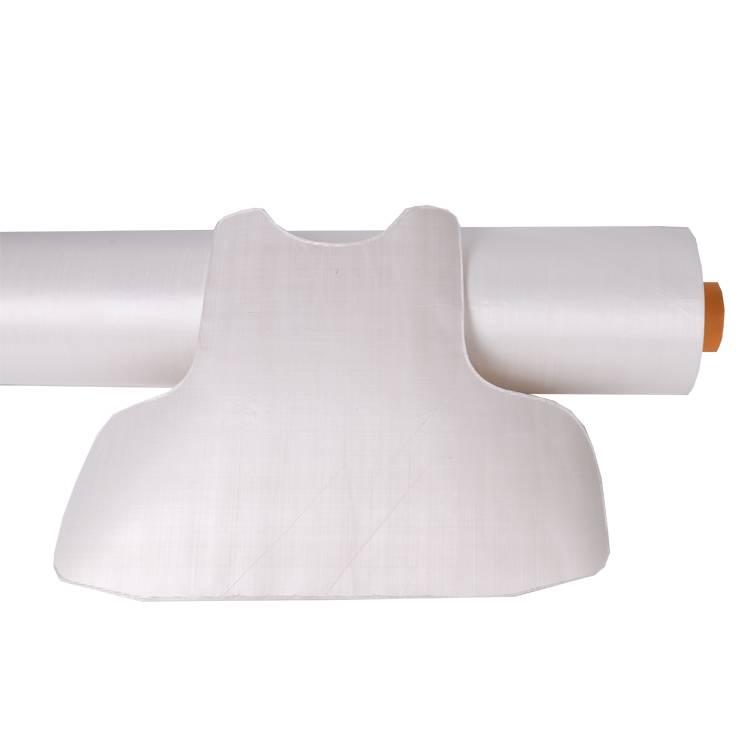
UHMW-PE: The Emergent Protector
- Advantages: With exceptional structural stability and resistance to degradation, UHMW-PE has become essential for bulletproof vests.
- Characteristics: Its low density and high impact strength make it an attractive option for lightweight, resilient gear.

Limitations of UHMW-PE: The Double-Edged Sword
- Heat Resistance: Poor heat resistance limits its use in high-temperature environments.
- Creep Resistance: UHMW-PE may deform under sustained stress, affecting its suitability for equipment requiring stability.
Conclusion:
Aramid and UHMW-PE, with their distinct properties and limitations, hold significant positions in the bulletproof equipment market. The choice between them depends on application requirements and environmental conditions. As technology advances, further evolution of these materials is expected, enhancing protection and versatility in PPE.
Final Thoughts:
The ongoing saga of Aramid and UHMW-PE reflects a narrative of continuous advancement in material science, focusing on safety, sustainability, and ecological impact. These materials' legacy continues to protect those on the frontline between danger and security.